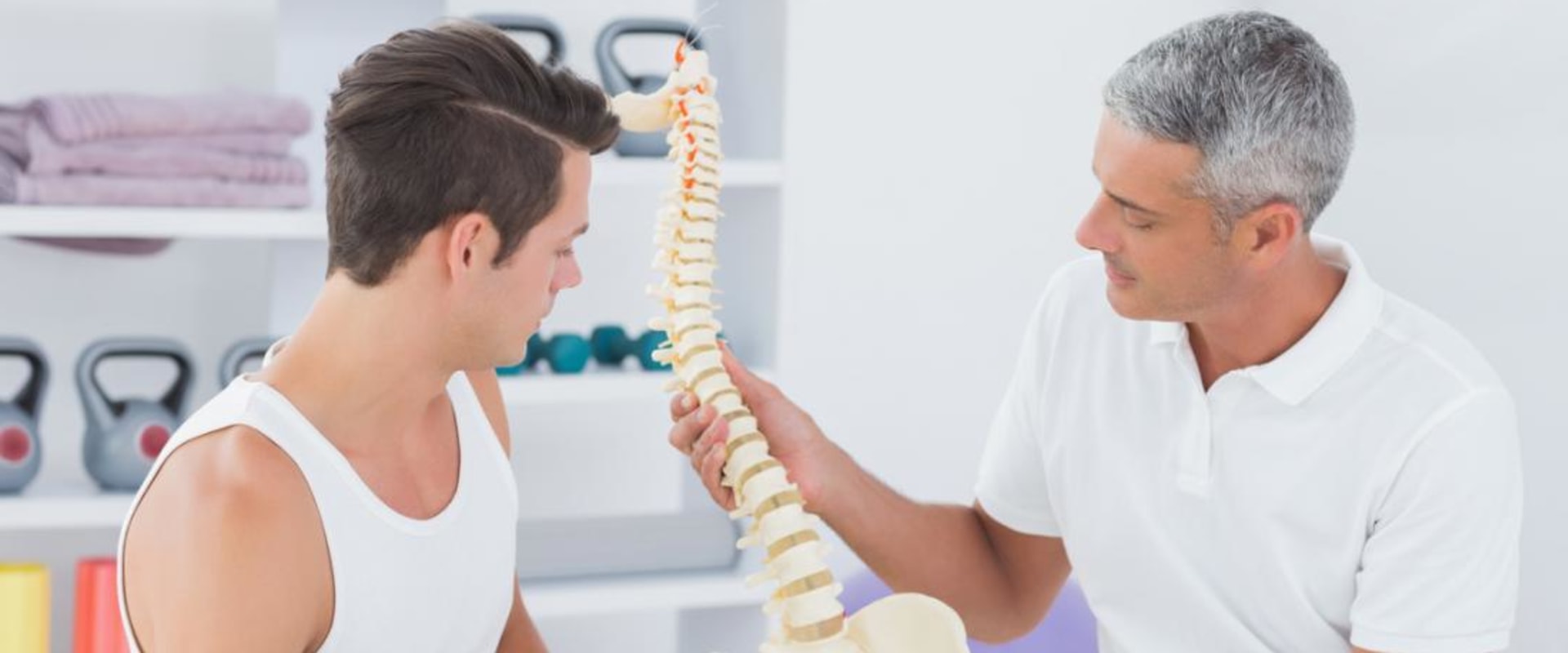
Osteopathy is a holistic branch of healthcare that focuses on the body’s musculoskeletal system, aiming to improve overall health by treating and strengthening the framework of bones, muscles, and joints. Unlike treatments that focus only on symptoms, osteopathy emphasizes the interconnectedness of body systems, helping patients achieve balance and long-term relief. Osteopaths use a combination of manual therapy, stretching, massage, and joint manipulation to support the body’s natural ability to heal itself. Because of this comprehensive approach, osteopathy is applied to a wide variety of conditions that affect not only physical movement but also general well-being.
Musculoskeletal Pain and Injuries
The most common use of osteopathy is in the treatment of musculoskeletal problems such as back pain, neck stiffness, shoulder tension, and joint pain. Patients who suffer from poor posture, sports injuries, or repetitive strain disorders often turn to osteopathy for relief. Techniques such as soft tissue massage and spinal adjustments work to restore mobility, reduce inflammation, and alleviate chronic discomfort. Unlike painkillers that temporarily mask symptoms, osteopathy seeks to identify the root causes of pain, providing longer-lasting results and helping patients prevent future injuries.
Headaches and Postural Strain
Osteopathy is also used to treat conditions that are indirectly linked to the musculoskeletal system, such as tension headaches and migraines. Many of these issues stem from muscular tension in the neck and shoulders or spinal misalignment. Through gentle manipulation and corrective exercises, osteopaths help reduce pressure on nerves and improve blood flow, which can significantly reduce headache frequency and intensity. This approach is particularly effective for individuals whose headaches are triggered by poor posture or long hours spent working at a desk.
Digestive and Respiratory Conditions
Although osteopathy is often associated with pain relief, its benefits extend to systems such as digestion and breathing. Osteopathic techniques that focus on improving chest and diaphragm mobility can enhance lung function and support people with asthma or chronic respiratory conditions. Similarly, by improving circulation and reducing abdominal tension, osteopathy can ease digestive discomfort such as bloating, constipation, or irritable bowel syndrome. These broader applications highlight osteopathy’s holistic nature and its aim to promote overall health, not just localized healing.
Stress, Circulation, and Sleep
Modern lifestyles often contribute to stress-related illnesses, poor circulation, and disrupted sleep patterns. Osteopathy addresses these issues by promoting relaxation through manual therapy, reducing muscular tightness, and improving blood flow. Patients frequently report better sleep quality and increased energy after osteopathic treatment, as the body becomes more balanced and less burdened by chronic tension. By supporting both the nervous and circulatory systems, osteopathy provides a natural alternative for people who want to manage stress without solely relying on medication.
Comparisons to Other Treatments
It’s important to note that osteopathy does not replace conventional medicine but instead complements it. Just as aesthetic procedures such as liposuctie abdominala bucuresti can address physical concerns related to body image and confidence, osteopathy focuses on restoring comfort, balance, and natural movement. Both approaches aim to improve quality of life but through very different means—one by reshaping physical appearance, the other by enhancing bodily function and overall health.
Conclusion
Osteopathy is used to treat a wide range of conditions, from chronic back pain and tension headaches to digestive disorders and stress-related issues. By focusing on the musculoskeletal system and its connections to other parts of the body, it provides holistic solutions that improve mobility, circulation, and overall well-being. While it works best as part of a comprehensive healthcare plan, osteopathy offers a natural and effective way to manage discomfort, prevent injuries, and promote long-term health. Its versatility makes it a valuable treatment option for those seeking both physical relief and overall balance.